Bioinformatics Education and Tutorials

Introduction
When we understand genetic sequences DNA, RNA and protein, plus how they relate to each other, how DNA acts as an information database on how to build all living things, we can start to ask deeper questions about a heritage, infections, allergy, diseases in general, genetic mutations, relationship of all species, how to increase food crop yield, how to design personalised medicine, tailor make genes and so on. The list is long.
The tutorials emphasize the underlying fundamental principles and ideas instead of first focusing on many details. The understanding of the concepts is the key to the learning process. One can always look up the details anytime, besides we would not remember all of them either.
Each tutorial is a self-contained entity. Because bioinformatics is a cross-disciplinary field, we have included pointers to relevant Biology and Biomedicine sections, e.g., such as immunology, microbiology, virology, genetics, infectious diseases and population biology.
Furthermore, each tutorial includes a list of prerequisites with links to those sections. Last but not least, many tutorials contain a wealth of images, animations or videos as required to enhance the learning experience and make it enjoyable.
The best part of it is that you can use the material for free for any non-commercial purpose. Go ahead and explore!
Don’t forget to study the history also! Why? Learn. To both study and value, the steps pioneers daringly took to where no one has gone before, to open new doors. Doors to brand new places for others to explore. To change the world for generations to come.

History S
History from the 19th century to the 21st century. From Mendel and Miescher to the birth of bioinformatics and the completion of the human genome. The bold steps taken by great scientists to the unknown.
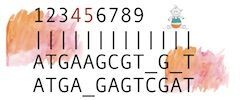
Introduction to sequence comparison S
A starter level primer introduces the ideas of a match, mismatch, gap, insertion, deletion, indel, global and local alignments.

Pair-wise sequence alignment B
A basic level tutorial, introducing DNA and protein sequence alignments, substitution matrices and discusses the bases of sequence similarity.

Pair-wise sequence alignment methods I
An intermediate level tutorial, introducing pair-wise global (Needleman-Wunch) and local (Smith-Waterman) sequence alignment methods without advanced mathematics and discusses the main implementation aspects.

Construction of substitution matrices I
An intermediate level tutorial of BLOSUM and PAM substitution matrices describe their detailed, step by step construction.

DNA Sequence Alignment How to I
Detailed step-by-step instructions on how to construct DNA scoring matrices and how to optimize them to target different sequence similarity levels. After this tutorial, you can design your DNA scoring matrices.

How to select the right substitution matrix? I
A comprehensive tutorial explains the effects of selection of scoring matrices for pair-wise sequence alignments and database searches. This tutorial also explores the impact of a 'wrong' scoring matrix selection and how all scoring schemes have explicit or implicit optimal target similarity.

Homology, analogy, similarity I
This tutorial is an intermediate level tutorial on homology. We cover homology classes, hierarchies, analogous processes, and the concept of deep homology, among others.

Introduction to Information Theory and Its Applications to DNA and Protein Sequence Alignments B
A basic level tutorial describes what information and entropy is. Detailed step-by-step instructions on how to calculate information and entropy content for DNA and protein sequences. A basic introduction to sequence logos and their relation to information contained in multiple sequence alignments.
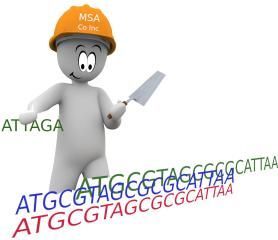
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) Methods I
Currently working on this tutorial. I am planning to complete this by the end of the next week.
Dr M

The Principles of WGS Sequencing and Automated Fragment Assembly I
Although I wrote this a long time ago, the article provides a fascinating insight into the era when the International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium and Celera Genomics reported the drafts of the human genome project and later completed by April 2003.

Introduction to sequence assembly S
A starter-level tutorial. It introduces the essential principles of hows and whys of the sequence assembly.

Genome assembly Quality Metrics I
A sequence assembly can go wrong in many ways. Thus, we must assess both the correctness and completeness of an assembly. We go through the most common assembly quality metrics. N50, k-mers, and BUSCO.

Sequence Assembly Practical I
In this practical, we learn the intricacies of assembling a ~5 Mb haploid genome using long read PacBio sequencing technology.
Genotype Imputation I
Genotype imputation software tools are an essential part of genetics research. These tools are used to fill in missing genetic information in a dataset, especially when working with extensive datasets where some genetic information is missing.

Best bioinformatics tools for beginners B
Overview of common bioinformatics tools and resources.

Critical thinking I
Coming soon...

Applications of bioinformatics in various fields I
Bioinformatics applications use computational tools and methods to analyze biological data. These applications have a wide range of uses, including...

History and major milestones in bioinformatics B
Over the past few decades, numerous milestones in bioinformatics have significantly impacted our understanding of biology and the development of new therapies and treatments.
The scientific method B
The scientific method is the key to unlocking the mysteries of the world around us. It's a powerful tool scientists, researchers, and students use to investigate phenomena, test hypotheses, and gain knowledge.

Genome Sequencing S
Genome is the blueprint of life.
Coming soon...

Genome assembly II I
Coming soon...

Genome assembly III A
Coming soon...

The Diversity of Genomic Disorders I
Studying genomic disorders in exploring human health and disease presents a fascinating yet intellectually stimulating landscape. These disorders are defined by a broad spectrum of conditions resulting from variations within the human genome.

